


 Secure and encrypted payment processing
Secure and encrypted payment processing We ship to over 40 countries including the USA, UK, Europe, Australia and Japan
We ship to over 40 countries including the USA, UK, Europe, Australia and Japan Guaranteed refund or reship if you haven't received your order
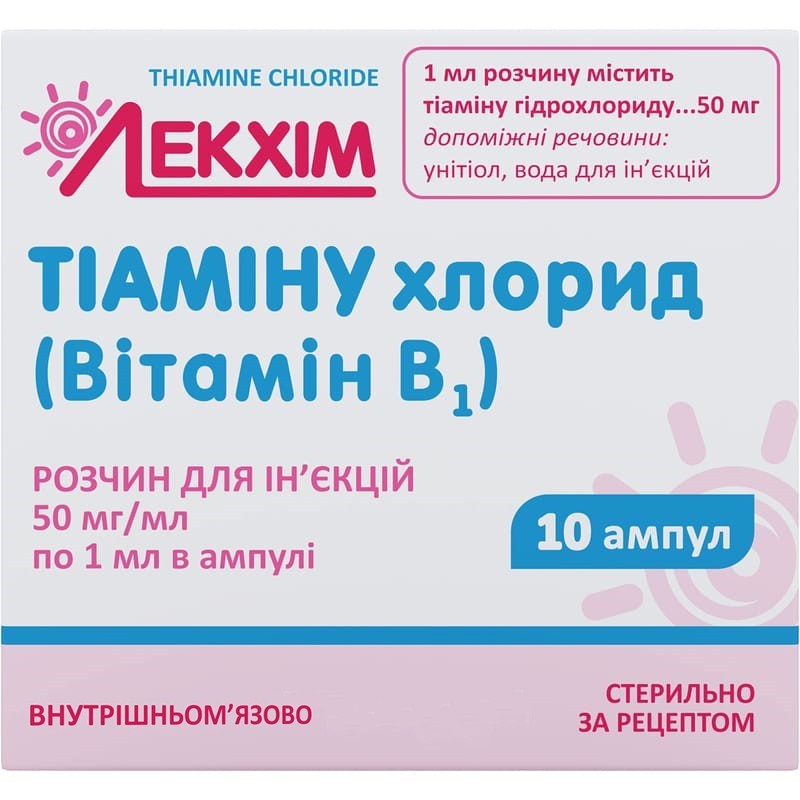
Guaranteed refund or reship if you haven't received your orderActive substance: thiamine hydrochloride;
1 ml of the solution contains 50 mg thiamine hydrochloride;
excipients: unitiol, water for injection.
Injection.
Basic physical and chemical properties: a clear solution from colorless to yellowish or greenish-yellowish.
Simple vitamin B1 preparations. thiamine (vitamin B1). code atx a11d a01.
Pharmacodynamics
Thiamine Chloride (Vitamin B1) - a synthetic preparation of water-soluble vitamin B1. In the body, as a result of phosphorylation processes, it turns into cocarboxylase, which is a coenzyme of many enzymatic reactions.
The drug resumes vitamin B deficiency1, which plays an important role in metabolism and neuro-reflex regulation, affects the conduct of nervous excitation in synapses, and exhibits a ganglion-blocking and curariform effect.
Pharmacokinetics
After intramuscular administration, the drug is rapidly absorbed. Phosphorylation occurs in the liver. Accumulates in the liver, heart, brain, kidneys, spleen. Eliminated by the kidneys and intestines, approximately 8-10% - unchanged.
Hypo-and vitamin deficiency B1 (including in patients on probe nutrition, on hemodialysis, suffering from malabsorption syndrome). as part of complex therapy: neuritis, polyneuritis, sciatica, neuralgia, peripheral paresis and paralysis, neuropathies (diabetic, alcoholic), encephalopathy (including Wernicke-Korsakov encephalopathy), neurasthenia, chronic liver damage, myocardial dystrophy, and gastric ulcer and duodenum, intestinal atony, endarteritis, dermatosis (eczema, atopic dermatitis, pyoderma, psoriasis, lichen planus) with neutrophic changes and metabolic disorders.
Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug, allergic diseases, idiosyncrasy, premenopausal and menopausal periods in women.
Thiamine can weaken the effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants (suxamethonium), choline derivatives, adrenergic agonists, sympathomimetics. long-term treatment with anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine), as well as combined use with digoxin, indomethacin, antacids, can lead to thiamine deficiency. thiosemicarbazone and 5-fluorouranyl inhibit thiamine activity. the use of caffeine, drugs that contain sulfur and estrogens, increases the need for thiamine, ethanol reduces the absorption rate of thiamine.
The use of cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine complicates the conversion of thiamine into a phosphorylated biologically active form and enhances its allergenic effect. The simultaneous parenteral administration of thiamine with pyridoxine (vitamin B is not recommended6) or cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12);
The use with adrenomimetics, sympathomimetics weakens their therapeutic effect.
Thiamine is unstable in alkaline and neutral solutions - purpose with carbonates, citrates, barbiturates, s Cu2+, iodide, ammonium iron citrate, thiamic acid is not recommended.
With caution, a drug should be prescribed with increased excitability of the nervous system, hyperacid forms of duodenal ulcer.
The injection form of the drug must be used in the treatment of patients with malabsorption in the intestines or with a resection of the stomach, if it is impossible to take thiamine in tablet form (nausea, vomiting,pre- and postoperative period), as well as in severe forms of the disease or at the beginning of treatment to more quickly achieve a therapeutic effect.
Due to the low pH of the solution, injections can be painful. In patients with alcoholism may increase the symptoms of side effects of the drug. You can not use the drug as a substitute for a balanced diet - only in combination with diet therapy. If you are allergic to thiamine from the patient’s diet, it is recommended to exclude rice, buckwheat, meat, bread (containing wholemeal flour).
The use of thiamine in high doses can distort the results when determining theophylline in blood serum by spectrophotometric method and urobilinogen using Ehrlich reagent.
It is recommended to start parenteral administration with small doses (not more than 0.5 ml for adults), and only with good tolerance, enter higher doses.
Before parenteral use of a solution of thiamine chloride, a skin test is mandatory for an individual sensitivity to the drug. Anaphylactic reactions develop more often after intravenous administration in high doses.
It is advisable to do thiamine injections no earlier than 12 hours after the injection of pyridoxine.
With intramuscular administration, the drug should be injected deep into the muscle, with intravenous administration, slowly.
Daily Vitamin B Requirement1: for adult men - 1.2–2.1 mg, for the elderly - 1.2–1.4 mg, for women - 1.1–1.5 mg with the addition of 0.4 mg to pregnant women and 0.6 mg - for women during lactation, for children, depending on age, 0.3-0.5 mg.
With Wernicke encephalopathy, thiamine must be used before glucose administration.
Thiamine can weaken the effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants, adrenolytic and sympathomimetic agents.
After the injection, control is necessary for 30 minutes due to the possibility of severe allergic reactions.
Use during pregnancy or lactation is possible in recommended doses under the supervision of a physician.
During treatment, care should be taken when driving vehicles and working with complex mechanisms in connection with the possibility of developing adverse reactions from the nervous system.
Assign intramuscularly (deep into the muscle).
Adults are prescribed 25-50 mg (0.5-1 ml of the drug) 1 time per day, daily.
The introduction begins with small doses [not more than 25 mg (0.5 ml)], higher doses [50 mg (1 ml)] are administered only if they are well tolerated. The course of treatment is 10-30 injections.
With Wernicke-Korsakov encephalopathy, 50–100 mg (1-2 ml) are used 2 times a day intramuscularly until clinical improvement. The likelihood of an allergic reaction to vitamin B administration should be considered.1.
For children from the age of 8 years, 12.5 mg (0.25 ml) are used once a day, daily. The course of treatment is 10-30 injections.
Children usually use a 2.5% solution of thiamine hydrochloride. It is possible to administer a 5% solution to children over the age of 8 years.
Symptoms: may increase the symptoms of side effects of the drug - hypercoagulation, impaired purine metabolism.
Treatment: drug withdrawal; symptomatic therapy.
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, palpitations, collapse.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, anxiety, paresthesia.
From the side of the organs of vision: damage to the optic nerve.
From the respiratory system: shortness of breath, shortness of breath.
From the alimentary canal: difficulty swallowing, nausea, intestinal hemorrhages.
On the part of the immune system: rash, itching (including at the injection site), dermatitis, hyperemia, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospastic syndrome with seizures, anaphylactic shock.
From the hepatobiliary system: impaired activity of liver enzymes.
General disorders: increased sweating, chills, tremors, general weakness, swelling, fever.
Others: the phenomenon of synaptoplegia - the ability of thiamine to form complexes with various mediators may be accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias, impaired contraction of skeletal (including respiratory) muscles, and depression of the central nervous system; thiamine contributes to the development of staphylococcus resistance to antibiotics.
The solution “thiamine chloride (vitamin B1) ˮ should not be mixed with solutions that contain sulfites, with nicotinic acid - thiamine is destroyed; with benzylpenicillin or streptomycin - the destruction of antibiotics occurs; with carbonates, citrates, barbiturates, with cu2 +, iodides, tannic acid - thiamine is unstable in alkaline and neutral solutions.
2 years.
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
1 ml in an ampoule. 10 ampoules in a pack of cardboard with partitions; or 5 ampoules in a single-sided blister, 2 blisters in a pack of cardboard.
On prescription.
Private joint-stock company "lekkhim-kharkov".
Ukraine, 61115, Kharkiv region, Kharkiv city, Severin Pototsky street, 36.