

 Secure and encrypted payment processing
Secure and encrypted payment processing We ship to over 40 countries including the USA, UK, Europe, Australia and Japan
We ship to over 40 countries including the USA, UK, Europe, Australia and Japan Guaranteed refund or reship if you haven't received your order
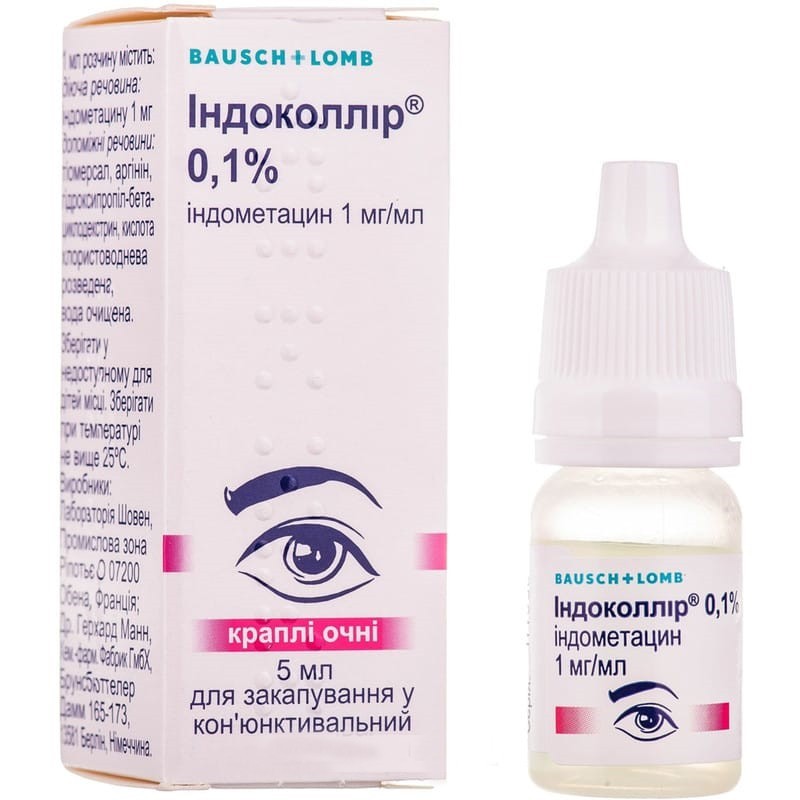
Guaranteed refund or reship if you haven't received your orderophthalmic drug belongs to the group of NSAIDs. when applied topically, it has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects; inhibits the activity of prostaglandinsynthetase. active substance - indomethacin, belongs to the indole group of NSAIDs.
Pharmacokinetics There is no data.
For topical use in adults in ophthalmology, the dose, frequency and duration are determined individually.
Elimination of miosis during surgery: 1 drop 4 times a day the day before surgery and 1 drop (4 times) 3 hours before surgery.
For the prevention of inflammatory processes after surgery for cataracts or after surgery on the anterior chamber of the eye: 1 drop 4-6 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely; instillation should be started 24 hours before surgery.
To eliminate eye pain after photorefractive keratectomy: 1 drop 4 times a day for the first few days after surgery.
Directions for use. For instillation of the drug, the lower eyelid should be slightly pulled back and 1 drop of the solution should be instilled into the conjunctival sac of the eye, while looking up.
Iii trimester of pregnancy; a detected allergy to indomethacin or drugs with a similar effect, for example, other NSAIDs or acetylsalicylic acid; patients with a history of asthma attacks caused by acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs; active peptic ulcer; severe hepatocellular damage; severe renal failure.
As a rule, this drug should not be used in combination (see INTERACTIONS) with oral anticoagulants; other NSAIDs (including high doses of salicylates (3 g / day for adults); diflunisal; heparin; lithium; high doses of methotrexate; ticlopidine.
The reactions that are sometimes noted are a slight, transient sensation of burning or acute pain and / or visual impairment after instillation.
Reactions that are rarely detected are hypersensitivity reactions, accompanied by itching and redness; there is evidence of a possible manifestation of acute asthma-like symptoms of respiratory tract damage: difficulty breathing, suffocation; photosensitivity is possible; spot keratitis.
In isolated cases, NSAIDs can cause a negative effect on the cornea, such as keratitis and corneal ulcers, which may be complicated by its perforation, especially if the drug is used in patients with a weakened cornea.
This drug contains an organomercury compound that can cause an allergic reaction,
Cautions regarding use. In case of development of symptoms of hypersensitivity, drug treatment should be discontinued.
If there is a risk of developing an eye infection, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
NSAIDs can slow corneal healing.
NSAIDs can increase bleeding in the tissues of the eye during surgery, especially in patients with a tendency to bleed or in patients taking other drugs that can prolong bleeding.
It is not recommended to wear contact lenses during treatment with the drug.
If other drops for the eyes are used at the same time during Indocollyre treatment, the interval between instillations should be at least 15 minutes.
When instilling, do not touch the eye or eyelids with the tip of the dropper bottle.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding. The effect of the drug on the occurrence of developmental deficiencies in humans has not been reported. However, additional epidemiological studies are needed that confirm the absence of any risk.
The use of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in the III trimester of pregnancy can have such consequences for the fetus:
Therefore, indomethacin can be prescribed in the first 5 months of pregnancy only if absolutely necessary. Starting from the 6th month of pregnancy, the use of indomethacin is contraindicated.
The period of breastfeeding. It is known that NSAIDs pass into breast milk, so their use during lactation should be avoided.
Children. Special studies involving children have not been conducted, so the drug is not recommended for use in pediatric practice.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or working with other mechanisms. Patients whose visual acuity decreases immediately after instillation should temporarily refrain from driving vehicles or working with other mechanisms.
To avoid mixing and interaction of active substances, the interval between instillation of different drops should be 15 minutes
If necessary, indomethacin in the form of eye drops can be combined with eye drops that contain corticosteroids.
Although after instillation of eye drops only a small amount of indomethacin enters the systemic circulation, the interaction between the drugs does occur. Therefore, it is desirable to take into account the interaction that is observed with the use of NSAIDs.
The following combinations are not recommended.
If such a combination is necessary, then in this case, clinical and laboratory observation is required.
If such a combination is necessary, then clinical observation and laboratory monitoring of unfractionated heparins are required.
If such a combination is necessary, then control of the level of lithium in the blood and dose adjustment are required during the combined treatment and after the withdrawal of NSAIDs.
If such a combination is necessary, careful monitoring of clinical and laboratory parameters, including bleeding time, is required.
Precautions
Hydration of patients and monitoring of renal function at the beginning of treatment are required.
During the first weeks of combination treatment, a weekly complete blood count is required. Even with minor changes in renal function, careful monitoring of the condition of patients, especially the elderly, is necessary.
Strengthen clinical monitoring and frequently check bleeding times.
Any antacids should be used separately from indomethacin (if possible, then with an interval of ≥2 h).
Combinations to consider
Reducing the antihypertensive effect (NSAIDs suppress vasodilator prostaglandins).
Perhaps an increase in the manifestations of side effects. symptomatic treatment.
At temperatures up to 25 ° C.